The novel Coronavirus also called COVID-19 originated in Wuhan, China in December 2019 and spread across the world. As the symptoms are also related to pneumonia patients, it is badly needed to diagnose accurately whether it is COVID-19 or Pneumonia for better treatment and avoid the transmission of COVID-19. The limited quantity of resources and lengthy diagnosis process encouraged us to come up with a Deep Learning model that can aid radiologists and healthcare professionals. In this study, we proposed a Deep Learning Model to automatically detect COVID-19, Pneumonia, and Normal patients from chest X-ray images. The proposed model is based on CNN architecture on a secondary dataset. The model has been trained and tested on the prepared dataset and the experimental results show an overall accuracy of 95.16%, and more importantly, the precision and recall rate for COVID-19 cases is 93.0% and 96.5% for 3-class cases (COVID vs Pneumonia vs Normal). The preliminary results of this study look promising and can be further improved by the different architecture and more training data.
Objectives
The specific objectives of the study are as follows:
- To detect 3 classes of patients using chest X-ray images
- Fast and accurate diagnosis of the disease to avoid transmission of covid-19
- Decrease the loss of life to faulty diagnosis
- Getting proper treatment for the proper disease
Dataset
For the purpose of the experiments, X-ray images were collected from secondary sources. A collection of X-ray images from selected from Kaggle’s repository was selected. This dataset consists of X-Rays from 3617 individuals with COVID-19, 4991 from healthy individuals which are labeled as normal, and 1346 X-Rays from individuals with viral pneumonia. All the images are in the Portable Network Graphics (PNG) file format, and with a resolution of 299-by-299 pixels with 3 color channels red, green, and blue.
Image Processing
Using raw images in deep learning models leads to poor performance in classification, whereas preprocessing techniques increase the performance. The preprocessing techniques are also essential to speed up the training procedure. All the images were resized to 150×150 pixels for fast computation purposes. At this stage the amount of data is divided into training and testing with a data division of 80:20. After splitting the data training set contains 7960 images and 1991 for testing. The distribution of data used is 80:20 because other proportions will not be sufficient for the validation process. All images were normalized according to the pre-trained model standards.
CNN Model Architecture
Our proposed model is based on five basic components, namely convolutional layer, pooling layer, flatten layer, dense layer, and activation function. The components are used in different layers of our proposed model. A detailed discussion of each basic component is given below.

Model Summary

We have used the Adam optimizer for weight updates, categorical cross-entropy loss function, and selected learning rate to compile the model. The model was trained with 20 epochs and batch size 64.
Results

The model achieved the best classification accuracy of 98.90% on train data after 20 epochs. Each epoch was done by batch size 64. The model showed a validation accuracy of 95.16% with the same epoch and batch size. The validation accuracy is the accuracy based on the test data.
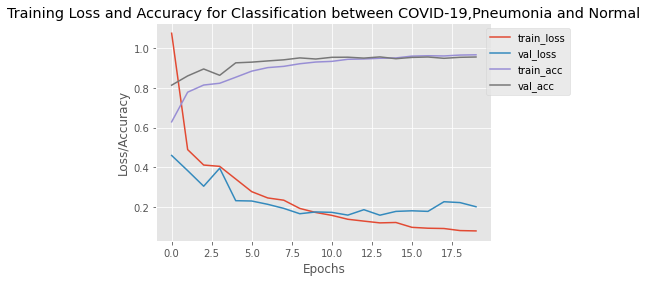
The figure displays the training and validation loss and accuracy of the model over epochs. It indicates a smooth training process during which the loss gradually decreases and the accuracy increases. Moreover, it can be observed that the accuracy of both training and validation do not deviate much from one another in most cases, a phenomenon that can also be observed for the training and validation loss, indicating that the model is not overfitting.

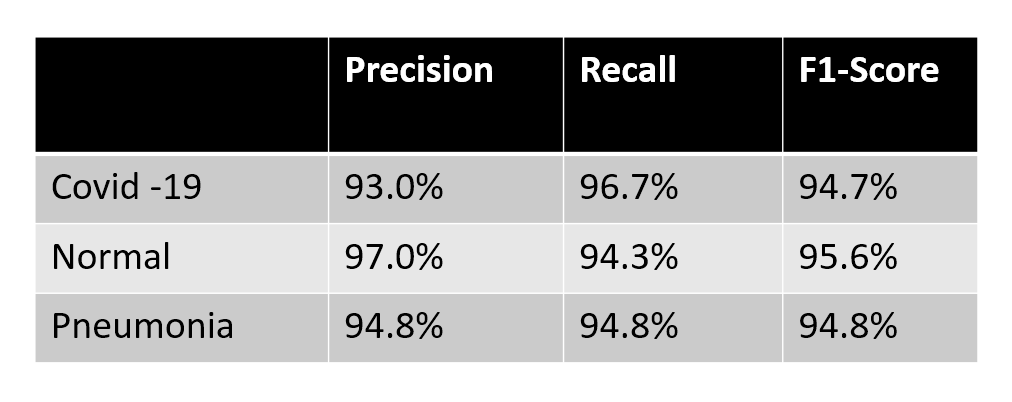
The performance metrics mentioned in the figure are the top metrics used to measure the performance of classification algorithms. The proposed model achieved an average accuracy of 92.95%, while the data is actually COVD-19 and predicted as COVID-19. The percentage of actually Normal and also predicted as normal is 97.01%. The next class that is actually Pneumonia and Classified as Pneumonia is 94.80%.
Discussion
Based on the results, it is demonstrated that the deep learning model may have significant effects on the automatic detection of covid-19 and pneumonia from X-ray images, related to the diagnosis of Covid-19.
The present work contributes to the possibility of a low-cost, rapid, and automatic diagnosis of the Coronavirus disease. It is to be investigated whether the extracted features performed by the CNNs constitute reliable biomarkers aiding in the detection of Covid-19. Also, despite the fact that the appropriate treatment is not determined solely from an X-ray image, an initial screening of the cases would be useful, not in the type of treatment, but in the timely application of quarantine measures in the positive samples, until a more complete examination and specific treatment or follow-up procedure are followed.
Limitations & Future Work
Some limitations of the particular study can be overcome in future research.
- The different architectures of deep learning like VGG16 / VGG19 / Alexnet or others can be implemented.
- Due to time limitations and lack of resources can’t compare with multiple models
- In the future, we can implement the model with real data.
Conclusion
X-ray images play an important role in the diagnosis of COVID-19 infection from other pneumonia as advanced imaging evidence. Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms and radionic features derived from chest X-rays can be of huge help to undertaking massive screening programs that could take place in any hospital with access to X-ray equipment and aid in the diagnosis of COVID-19, as all the processes can be done automatically, the cost is significantly decreased compared with the traditional method. In order to speed up the discovery of disease mechanisms, this research developed a deep CNN-based chest X-ray classifier to detect COVID-19, Pneumonia, and Normal X-Ray images. The classification accuracy of the proposed model is 95.16% for 3 classes which is the highest achieved accuracy to the best of our knowledge on the datasets used in the experiments. Our future goal is to overcome hardware limitations and implement multiple models to compare the performance with a greater number of existing methods.
